Crop Steering: Maximizing Yield with Precision Growth Control
How do indoor weed growers achieve such incredible yields from their crops? With all effective cannabis training techniques such as pruning and scrogging, one less well-known method is crop steering. Never heard of it? In simple terms, cannabis crop steering is a technique that allows growers to manipulate weed growth stages and patterns by practicing light, climate control, and root zone management. By doing so, growers ensure their plants develop in a way that maximizes yield.
We bet every grower wants to increase yields. So, don’t waste your time, let’s explore crop steering, including what it is, when, and how to use it to maximize cannabis yields.
Table of Contents
What Is Crop Steering
Crop steering isn’t just a buzzword - it’s a strategic way to control the life cycle of weed plants. It involves guiding crops through their growth stages, focusing on either vegetative growth (where the plant grows leaves and stems) or generative growth (where the plant focuses on flower and bud production). A minor change in the rules of the following factors can influence the plant’s physical and chemical growth response, giving you opportunities to steer plant growth vegetatively or generatively.
Light
Humidity
Temperature
Nutrients
CO2
Irrigation
How Does Crop Steering Work
Crop steering is a complex interaction you play with plant biology. It leverages the plant’s natural responses to its growing conditions, based on the understanding of how plants interpret their surroundings and distribute resources accordingly, to push the plant toward the desired development.
For example, higher temperatures and abundant phosphorus can stimulate root development during the vegetative phase, while cooler temperatures and calcium-rich conditions can promote stronger flower formation. Growers take advantage of these environmental cues, such as adjusting light intensity and nutrient balance, to guide plants into the desired growth phase, ensuring that the plant's energy is directed toward the most beneficial outcome for its current stage of development.
In addition to manual environmental control, modern technology also plays a big role in crop steering, with sensors and automated systems adjusting environmental conditions in real-time. By constantly monitoring factors like CO2 levels, light exposure, and nutrient content, these systems ensure plants receive precisely what they need at each stage, optimizing both growth and yield.

Vegetative Steering vs Generative Steering
Before jumping to specific crop steering techniques, you have to know the difference between the vegetative stage and the flowering stage.
Vegetative growth is the stage where the plant focuses on developing its root system, stem, and leaves. During this phase, the plant requires more water, nutrients, and light to support its rapid growth. To promote vegetative growth, growers can use a crop steering chart to adjust environmental conditions. For instance, maintaining a lower VPD (vapor pressure deficit) and higher humidity levels can encourage robust vegetative growth.

Generative growth is the stage where the plant shifts its focus to producing flowers and seeds. During this phase, the plant requires less water and nutrients but more light and CO2 to support flower development. To promote generative crop steering, growers can employ techniques such as reducing irrigation frequency, increasing light intensity, and maintaining a higher VPD. These adjustments help the plant allocate more energy toward flower production, resulting in higher-quality yields.
Balancing Vegetative and Generative Growth
Mastering crop steering means finding the perfect balance between vegetative and generative growth. Too much vegetative growth can lead to overly large plants with fewer fruits, while too much generative growth can result in weak plants that can’t support large yields. How to implement a balanced crop steering? Check out the following crop steering tricks!
Crop Steering in Environmental Control

Environmental control plays a crucial role in crop steering journey by influencing key factors such as light, temperature, humidity, and VPD to guide plants through vegetative and generative growth stages. Manipulating these factors helps growers optimize plant health and productivity. Here's a breakdown of the primary environmental factors used in crop steering:
Light: Adjusting the light cycle is essential, especially for photoperiodic plants like most cannabis strains. Switching to a 12-hour light cycle with 12 hours of darkness encourages flowering, while extended light exposure promotes vegetative growth. Fortunately, Spider Farmer is about to launch smart LED grow lights soon to let you freely adjust light schedules on the phone.
Temperature: Maintaining higher ambient temperatures encourages vegetative growth by keeping plants more active in developing roots, stems, and leaves. Conversely, lowering temperatures mimics seasonal changes, steering plants toward the generative phase.
Day-Night Temperature Difference: Altering the difference between day and night temperatures can control plant stretching. Large differences result in more spaced-out growth (inter-nodal spacing), while smaller differences produce a more compact plant structure.
Speed of Temperature Change: The rate at which the temperature shifts between day and night is also important. A slower transition can promote generative growth, while faster changes help maintain vegetative activity.
Pipe Temperature (if used): In greenhouse setups, controlling the temperature of pipes used for heating can further fine-tune the plant’s growth phase, especially during the generative stage.
Humidity: Higher humidity levels are favorable for vegetative growth as they reduce plant stress and support faster development. On the contrary, lower humidity during the generative phase signals the plant to focus on reproduction and fruiting. Here's a recommended grow room temp and humidity chart for cannabis cultivation.
|
Stage |
Temperature |
Humidity |
|---|---|---|
|
Seedling Stage |
Day temperature (lights on): 70–85°F Night temperature (lights off): 65–80°F |
75-85% |
|
Vegetative Stage |
Day temperature (lights on): 70–85°F Night temperature (lights off): 60-75°F |
45-55% |
|
Flowering Stage |
Day temperature (lights on): 65-84°F. Night temperature (lights off): 60-75°F |
35-45% |
|
Late Flowering Stage |
Day temperature (lights on): 64-75°F Night temperature (lights off): 60-68°F |
30-40% |
Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD): Managing VPD is key to regulating plant transpiration and water uptake. A higher VPD pushes plants towards the generative stage, while a lower VPD supports vegetative growth. Kindly refer to our online VPD calculator to know your current level and see if it fits the optimal range.
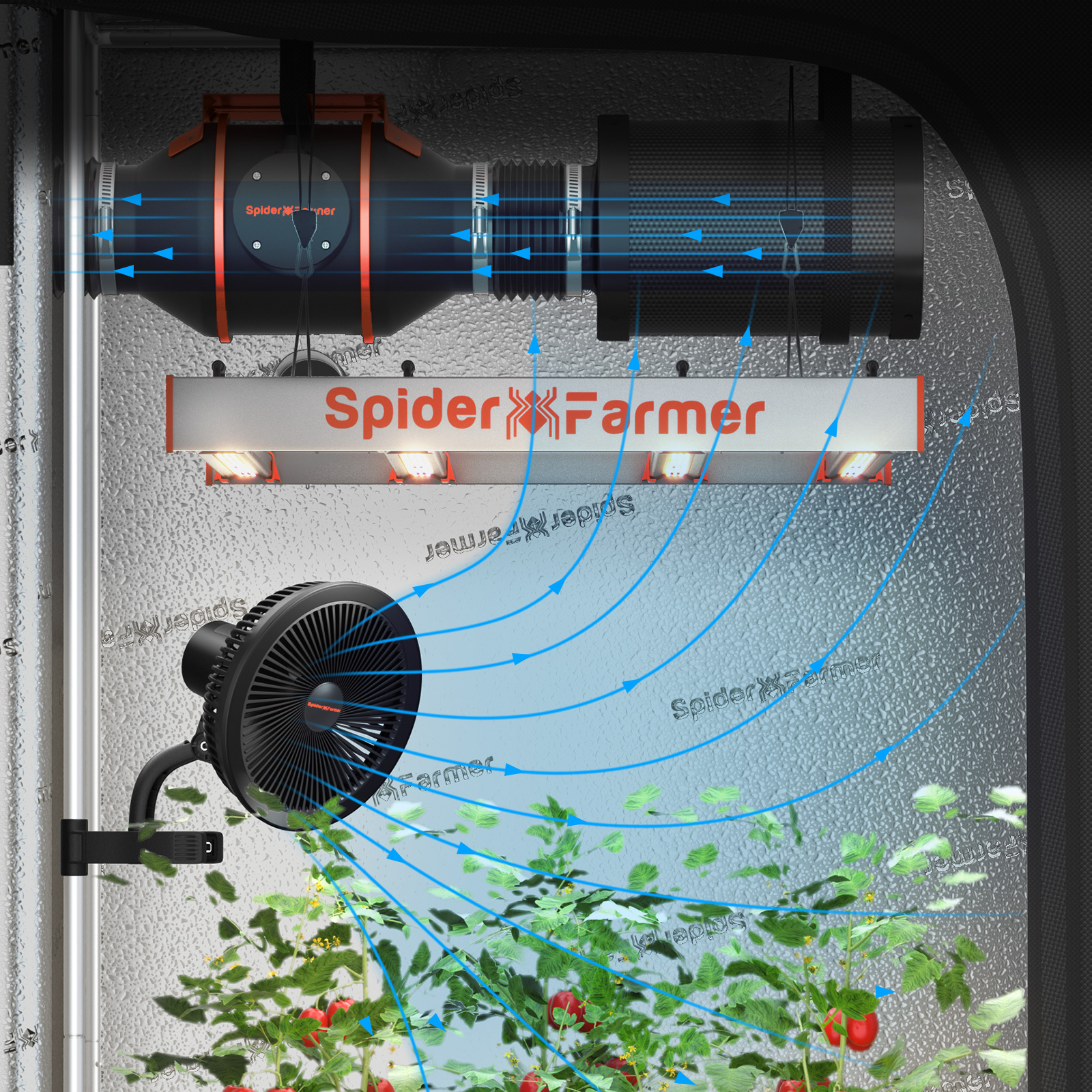
Ventilation and Air Exchange: Proper air circulation and ventilation help regulate temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels, all of which contribute to effective crop steering.
Crop Steering Cannabis in Nutrient
Nutrient uptake is a critical aspect of cultivating high-quality cannabis with optimal yields. When implementing crop steering in nutrients, the choice between organic and synthetic nutrient sources matters a lot. Organic nutrients release gradually, providing a steady and gentle supply of essential elements, while synthetic nutrients offer immediate and precise inputs, allowing for quick adjustments to the plant's needs. This selectivity in nutrient management is fundamental to crop steering, which involves manual environmental controls and irrigation practices to optimize plant growth outcomes.
What's more, you should think about the right balance and ratio of nutrients. During the vegetative stage, plants require higher levels of nitrogen to support leaf and stem growth. However, as the plant transitions into the flowering phase, the nutrient requirements shift towards increased phosphorus and potassium to encourage bud development. Tailoring nutrient formulations to align with the plant's developmental stages is essential to avoid cannabis deficiency and other health issues.
Crop Steering Cannabis in Irrigation

Crop steering through root zone conditions involves adjusting the volume, frequency, and timing of water delivery to control plant growth phases and maximize yield quality. By fine-tuning these factors, you can influence whether a plant enters a vegetative or generative phase, depending on its needs at different plant development stages.
During the vegetative phase, the goal is to promote strong leaf and root growth, which can be achieved by maintaining a higher water content (WC) in the root zone, reducing the dry-back periods between irrigations, and using frequent small irrigation events. If you are looking for an effortless irrigation system for your indoor plants, the Spider Farmer Automatic Drip Irrigation System is your ultimate choice. With an adjustable sprinkler head and 8 water emitters, you can easily decide the volume and timing of water delivered to your cannabis plants.
In contrast, during the generative phase, which focuses on flowering and fruit production, growers reduce the overall water content, increase the dry-back periods between irrigations, and adjust irrigation frequency to encourage reproductive growth. Techniques such as lowering substrate temperature and increasing electrical conductivity (EC) in the root zone help signal the plant to prioritize flower and fruit development.
When to Crop Steering
Depending on your goal, crop steering can be applied at any stage of plant growth to either encourage vegetative growth or shift the plant towards its generative (flowering or fruiting) phase. Many growers use a combination of vegetative and generative steering during the flowering cycle to maintain a balanced plant.
For example, as the plant matures and reaches the desired size, you can start steering it toward the generative phase. This involves reducing humidity, increasing the difference between day and night temperatures, and tweaking the light spectrum to prepare the plant for flowering or fruiting. Once the flowers have set and the first round of defoliation is complete, you may switch to a vegetative approach to keep the plant healthy and encourage flower bulking.
Some growers alternate between vegetative and generative methods to maintain plant balance, while others stick to vegetative steering until closer to harvest, at which point they switch to a more intense generative approach to finish the crop.
Conclusion
Crop steering is a powerful tool for modern agriculture, enabling growers to take control of their plant’s growth cycles and optimize yields. By balancing vegetative and generative growth and managing environmental factors such as light, temperature, and nutrients, growers can produce stronger plants and more abundant harvests. As technology advances, crop steering will likely become even more precise, helping to meet the growing demand for food in a sustainable way. If you have any trouble or problem regarding crop steering, leave a comment below!