9 Ways to Add Nitrogen to Soil
Indoor plants require all sorts of nutrients to grow well. Nitrogen, in particular, plays a leading role in photosynthesis, leaf development, building amino acids, and the overall health of plants. When your garden is showing signs of nitrogen deficiency, such as yellowing leaves and undersized crops, it's high time to add nitrogen to your soil. Assume you are in an emergency situation, how to add nitrogen to soil quickly without robbing your wallet?
We’ve got you covered - this article will explore various methods, both quick and slow, to enhance nitrogen levels in your garden soil. Let’s explore the 9 easy & fast ways to add nitrogen to soil.
Table of Contents
Signs of Nitrogen Deficiency
How can you tell if your plants lack nitrogen? Without a second opinion, the most accurate way is through testing. You can purchase a soil test kit or send your soil for professional analysis. However, in daily monitoring, the following signs also indicate nitrogen deficiency:
- Yellowing of older leaves (especially older leaves)
- Slowed or stunted growth
- Delayed maturity
- Smaller leaf size
- Purple or reddish discoloration
- Premature leaf shedding
- Delayed aging process
- Poor fruit or flower production
Once you notice these signs, don’t hesitate to add nitrogen to your soil with our methods below!
Adding Nitrogen to Soil
Once you feel there’s the need to feed the soil nitrogen, how to do it quickly and easily before everything gets too late? We have listed the 3 amazing ways below!
Urea Fertilizer
Urea fertilizer is one of the most concentrated sources of nitrogen and you can get it at pretty much all garden supply stores. Apply it at a rate of about 0.5 to 1 pound per 100 square feet and mix it well before adding it to the soil.

However, if you prefer a completely free way to exploit urea, diluted human urine is an option, a bit gross, though. You should water down the urine at 10:1 or 20:1 to make it perform just like the urea fertilizer.
Blood Meal
Blood meal is a dry, powdered form of animal blood, typically derived from livestock. It's a high-nitrogen organic fertilizer, containing about 12-15% nitrogen, making it particularly effective for adding nitrogen to the soil. Apply it at a rate of 1-2 tablespoons per plant to boost growth.

Animal Manure
Animal manure, particularly from chickens, cows, or horses, is rich in nitrogen. Ensure that it is well-composted before application to avoid burning plant roots. For example, use about 70 lbs of chicken manure per 100 sq ft of garden space.
You can also take one more step to make manure tea, which involves adding animal manure to a bucket and then filling it with water. The manure tea can be diluted further and applied to the nitrogen-deficiency soil.
So far, we have offered the fastest 3 ways to add nitrogen to soil. Either one of them can significantly fuel the soil with nitrogen. If you are not in a rush, the following 4 methods can build nitrogen levels over time.
Compost
Composting not only recycles kitchen scraps but also enriches your soil with nutrients, including nitrogen. It might take a bit longer, but it’s proven to build the overall fertility of your soil in the long run. Incorporate 1-2 inches of compost into your garden beds before planting or as a side dressing during the growing season. Remember the animal manure we mentioned above? You can add it to the compost for a better nitrogen boost!
Coffee Grounds
Similar to compost, coffee grounds are an excellent supply of nitrogen, aiding plants in absorbing nutrients and water more effectively. Whether you use regular or decaf coffee, most plants benefit from a teaspoon of used coffee grounds added to their soil.

Simply sprinkle them around your plants or mix them into the compost pile. Don’t expect overnight nitrogen increase with this method though, as it also takes time.
Fish Emulsion
Fish emulsion is an organic option that provides both nitrogen and phosphorus. While it may have an unpleasant odor, it effectively nourishes soil life when applied according to label instructions.
Dried Grass Clippings
Fresh grass clippings can serve as a nitrogen-rich mulch or soil amendment. Allow them to dry before applying to prevent matting and ensure even distribution. Then you can use grass clippings as mulch to cover the soil around your plants.
How to Prevent Nitrogen Deficiency
It’s not always the best approach to add nitrogen every time the soil is deficient. Instead, aim to create a nutrient-balanced environment for your plants. So, how can you build nitrogen-rich soil for the long term? Here are two natural nitrogen fertilizers you can try:
Planting Nitrogen-Fixing Crops
Leguminous plants such as beans, peas, and clover can naturally enrich the soil with nitrogen through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria in their root nodules. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use.
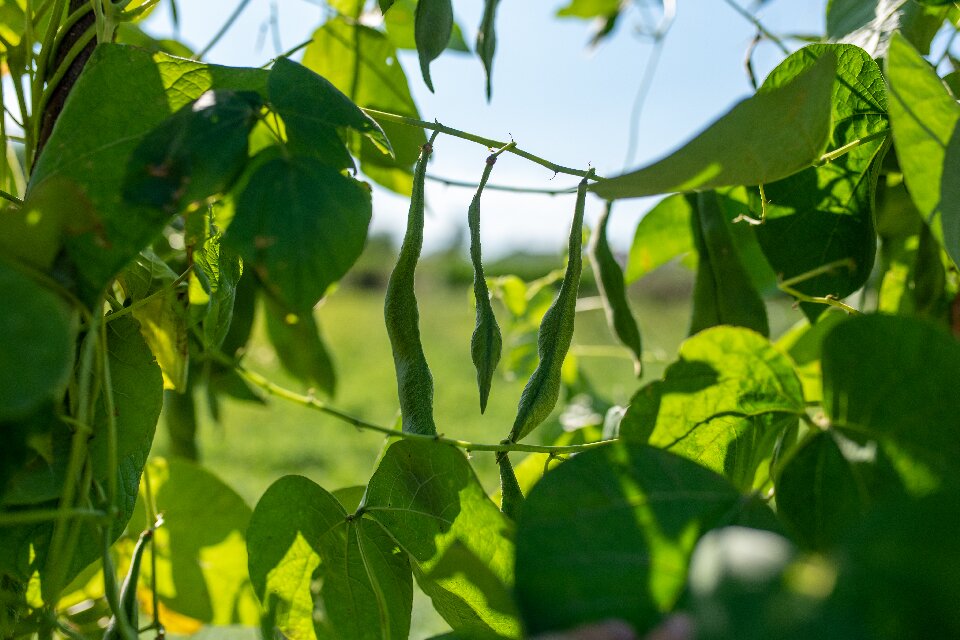

Once these legume cover crops are mature, you can till them into the soil to release the accumulated nitrogen. Additionally, legume cover crops create a dense canopy that shades the soil and suppresses grass growth.
Growing Alfalfa Meal
While alfalfa is most commonly recognized as a grass, growing this nitrogen-rich plant in your garden is a great way to naturally enhance nitrogen levels. As a substitute crop, alfalfa grows quickly, effectively blocking grass and developing deep roots that naturally aerate and break up clay soil, acting as natural tillers.
Alfalfa is also quite easy to cultivate. Simply spread the seeds evenly over the soil’s surface, water them, or lightly cover them with soil. Although it takes some time to establish, once it does, it can grow up to three feet tall.
What Does Nitrogen Do for Plants
As one of the three primary macronutrients that plants require, alongside phosphorus and potassium, what responsibility does nitrogen take? Here's a breakdown of what nitrogen does for your plants:
- Nitrogen is a major component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis. It helps plants produce lush, green foliage, which is especially important for leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach.
- Nitrogen is a building block of amino acids, the fundamental components of proteins, which are vital for nearly every aspect of plant function, including the structure of plant cells and the formation of enzymes.
- Adequate nitrogen levels help plants develop strong root systems. This is particularly important in the early stages of plant growth when roots are still developing.
- Nitrogen boosts the development of reproductive structures like flowers, seeds, and fruits. Plants receiving the right amount of nitrogen are more likely to produce larger fruits and more abundant flowers, which leads to better crop yields.
- Plants that are nitrogen-deficient are more prone to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors like drought. Healthy, nitrogen-rich plants are better equipped to withstand such challenges and continue growing.
Conclusion
Adding nitrogen to your soil is essential for promoting healthy vegetative growth. By using natural methods such as composting, planting legumes, or incorporating organic fertilizers like blood meal and fish emulsion, you can effectively enhance the nutrient profile of your garden soil.