If you find your plant growth stunted or you’re eager to see your garden flourish quickly, understanding how to accelerate plant growth is key. Whether you’re a professional gardener or just starting out, implementing effective strategies mentioned in this post can lead to healthier, faster-growing plants. Keep reading, find out the reasons why your plant growth stunted, learn how to fix stunted growth in plants, and further explore what plants are slowly growing and quickly growing.
Table of Contents
What Cause Stunted Growth in Plants?
Plant growth stunted is a common issue that can significantly affect their health and yields. Understanding the causes of this phenomenon is essential for gardeners and farmers alike. Here’s a detailed look at the primary factors resulting in stunted growth in plants.

Stunted Growth in Plants
- Nutrient Deficiencies: A lack of essential macronutrients such as Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium can lead to stunted growth in plants, This is because these nutrient deficiencies are vital for overall plant health and development. Besides, deficiencies in micronutrients like Iron, Manganese, and Zinc can impair critical functions like photosynthesis and enzyme activity, further hindering growth.
- Root Damage: The compromised roots with root damage are unable to effectively absorb water and nutrients from the soil, limiting the plant’s ability to sustain vital functions and resulting in weakened plant growth and overall health. Also, damaged roots can increase vulnerability to diseases, further exacerbating growth issues.
- Environmental Conditions: Environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures can stress plants, slowing their metabolic processes. Insufficient light reduces Photosynthesis, limiting energy production and overall growth. In these seasons, you’re highly recommended to supplement light with LED grow lights.
- Water Stress: Insufficient water supply causes dehydration, limiting the plant's ability to carry out essential processes like photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. Conversely, overwatering can lead to root rot, preventing roots from functioning properly and further restricting nutrient absorption. Both scenarios disrupt the plant's overall health and growth potential.
- Soil Quality: Poor soil structure and compaction restrict root development and limit access to water and nutrients. On the other hand, an unbalanced soil pH can influence plant nutrient availability, making it difficult for plants to absorb essential elements. Overall, suboptimal soil conditions hinder the plant's ability to thrive and grow effectively.
- Pest Diseases: Infections from fungi, bacteria, or viruses can disrupt essential physiological processes, further limiting growth and productivity. The stress caused by pests and diseases can also make plants more susceptible to other environmental challenges.
- Genetic Factors: Certain plant varieties may have inherent limitations in their growth potential or adaptability to specific environments. These genetic traits can affect the plant’s ability to effectively utilize nutrients, resist pests, or cope with environmental stressors. As a result, genetically predisposed plants may struggle to achieve optimal growth, even under ideal conditions.
- Growth Competition: Competition can lead to limited resources such as light, water, and nutrients. Overcrowding can inhibit individual plants' access to these essential elements, resulting in reduced growth rates and overall vigor. This struggle for resources can significantly limit a plant's ability to thrive and reach its full potential.
How to Make Plants Grow Faster?
The speed at which plants grow can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of plant, environmental conditions, and care practices. In this part, we’ll explore what helps plants grow.
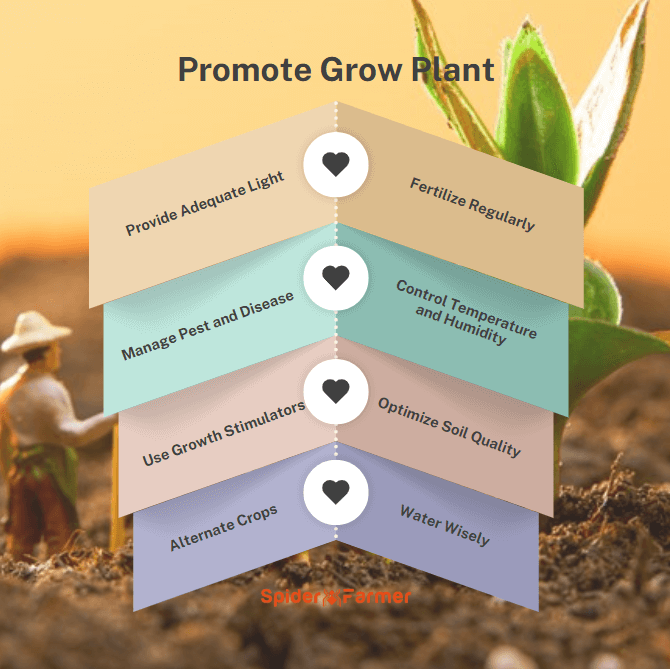
How to Make Plants Grow Faster?
Provide Adequate Light
The most important factor for plant growth is proper light. This is because adequate light directly impacts photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. During photosynthesis, plants use light to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, which are essential for their growth and development. Sufficient light enables plants to produce the energy needed for vital functions, such as cell division, nutrient uptake, and flowering. Besides, the right light intensity and duration help regulate other growth factors, such as flowering and fruiting cycles. Without adequate light, plants may become leggy, weak, and unable to thrive, ultimately stunting their growth.
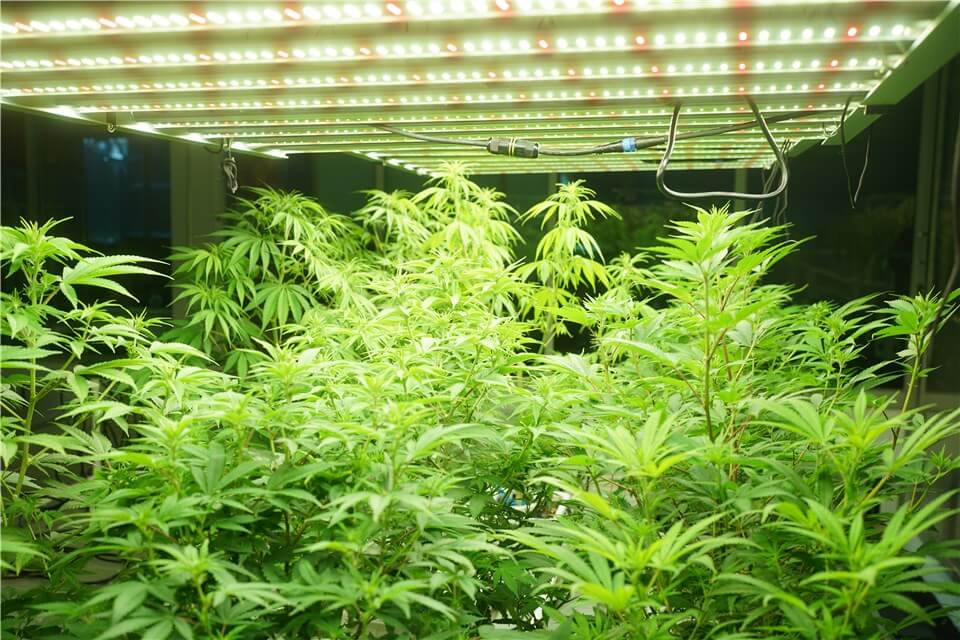

Adequate Light for Stunted Growth Plants
Control Temperature and Humidity
Temperature and humidity can directly influence a plant’s physiological processes. Optimal temperatures will promote metabolic activities, such as photosynthesis and respiration, enabling plants to utilize nutrients effectively and grow vigorously. If temperatures are too high or too low, plants may experience stress, leading to reduced growth rates or even damage.
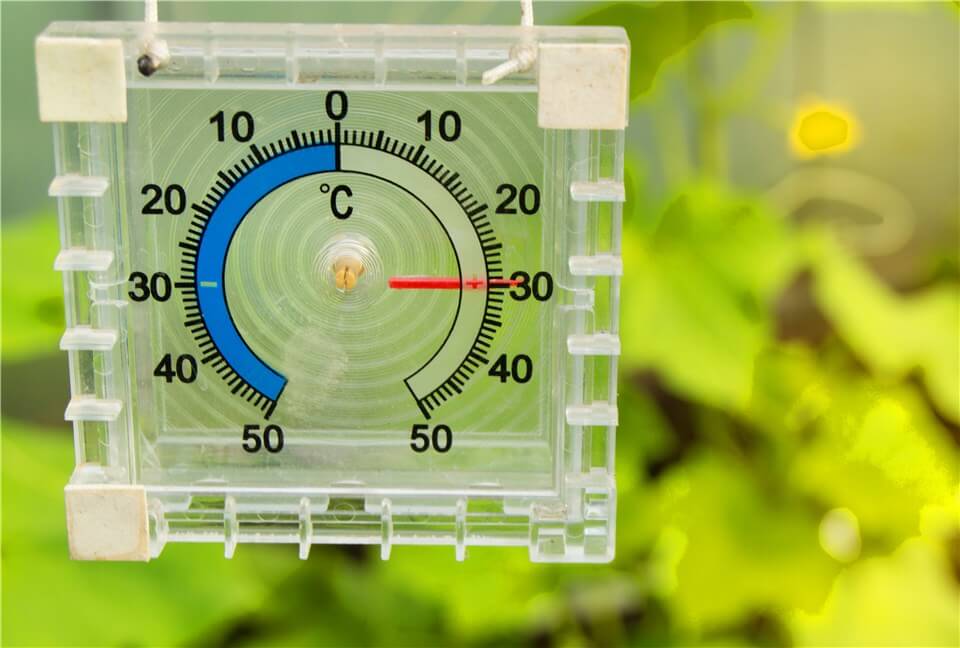

Control Temperature for Stunted Growth Plants
Humidity also plays a critical role; adequate humidity levels help maintain moisture in the air and soil, which is vital for water uptake and transpiration. High humidity can enhance growth in certain plants by reducing water loss, while low humidity can lead to wilting and hinder nutrient absorption. By maintaining the right temperature and humidity levels, gardeners can create an ideal environment that supports healthy plant development, enhances resilience, and maximizes yields.
Optimize Soil Quality
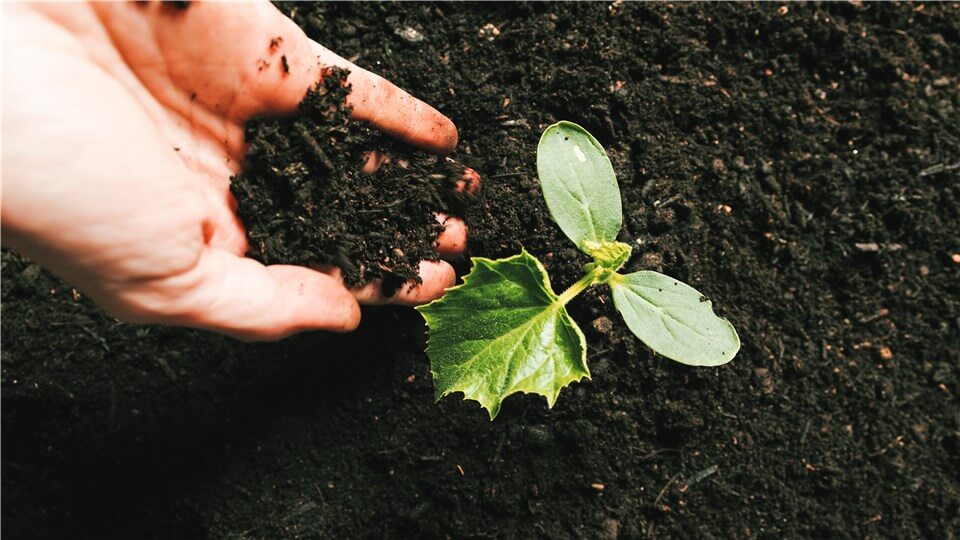

Improve Soil Quality for Stunted Grow Plants
Soil quality can directly affect nutrient availability, water retention, and root health. Healthy soil is rich in organic matter, which improves its structure and enhances its ability to retain moisture and nutrients. This ensures that plants have access to the essential elements they need for photosynthesis, growth, and development. Also, well-aerated soil promotes healthy root systems, allowing plants to absorb water and nutrients more effectively. Soil pH levels also play a crucial role; a balanced pH ensures that nutrients are accessible to plants. Furthermore, optimizing soil quality can enhance beneficial microbial activity, which contributes to nutrient cycling and overall soil fertility. By improving soil conditions, gardeners can create a thriving environment that supports robust plant growth and resilience.
Water Wisely
Watering wisely ensures that your plants receive the right amount of moisture to support their physiological processes. Adequate water is essential for photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cell expansion. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases, while underwatering can cause stress and wilting, both of which hinder growth.
By providing consistent and appropriate moisture levels, gardeners can promote healthy root development and enhance the plant's ability to absorb nutrients from the soil. Additionally, watering at the right times—such as early morning or late afternoon—helps reduce evaporation and allows plants to make the most of the water provided. Overall, wise watering practices create a balanced environment that fosters vigorous plant growth and resilience.
Fertilize Regularly
Fertilizing regularly encourages plant growth by supplying essential nutrients that may be lacking in the soil. Plants require a variety of macronutrients, such as Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, as well as micronutrients like Iron and Magnesium, to support key physiological processes, involving photosynthesis, root development, and flowering. Therefore, regular fertilization helps replenish these nutrients, ensuring that plants have what they need to grow robustly.
In addition, fertilizers can improve soil structure and enhance beneficial microbial activity, which further aids in nutrient availability and uptake. By providing a consistent supply of nutrients, gardeners can promote stronger, healthier plants that are better equipped to resist pests and diseases, ultimately leading to improved growth and higher yields. Regular fertilization tailored to specific plant needs creates an optimal growing environment and supports overall plant vitality.
Manage Pest and Disease
Infestations and infections can significantly hinder a plant’s health and development. Pests, such as aphids or caterpillars, can damage leaves, stems, and roots, reducing photosynthesis and nutrient absorption. Similarly, diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses can weaken plants, disrupt physiological processes, and even lead to plant death.
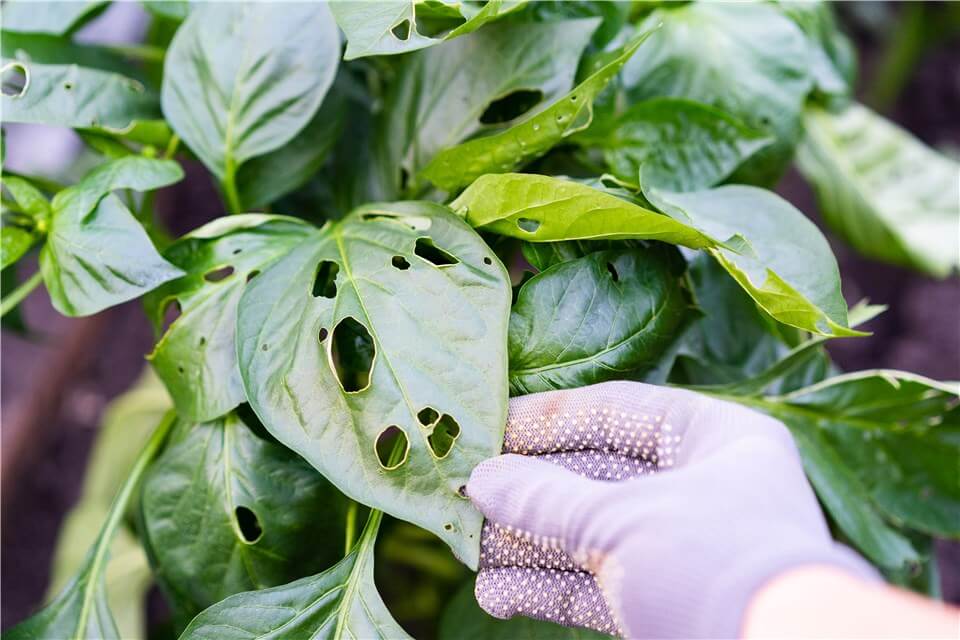

Manage Pest and Disease of Stunted Growth Plants
By actively monitoring and managing pest populations and disease outbreaks, gardeners can protect their plants from these threats, ensuring they have the energy and resources necessary for robust growth. Effective pest management strategies, such as using beneficial insects or organic pesticides, along with practicing good sanitation and crop rotation, can help maintain a healthy growing environment. Ultimately, protecting plants from pests and diseases fosters resilience, enhances growth, and contributes to a more productive garden.
Use Growth Stimulators
Growth stimulators are essential tools for enhancing plant growth and overall health, and they come in various forms. These substances, which can include natural or synthetic hormones, bio-stimulants, and fertilizers, help stimulate root growth, increase nutrient uptake, and improve overall plant vigor. For example, auxins can promote root development, while gibberellins can enhance stem elongation and fruit development.
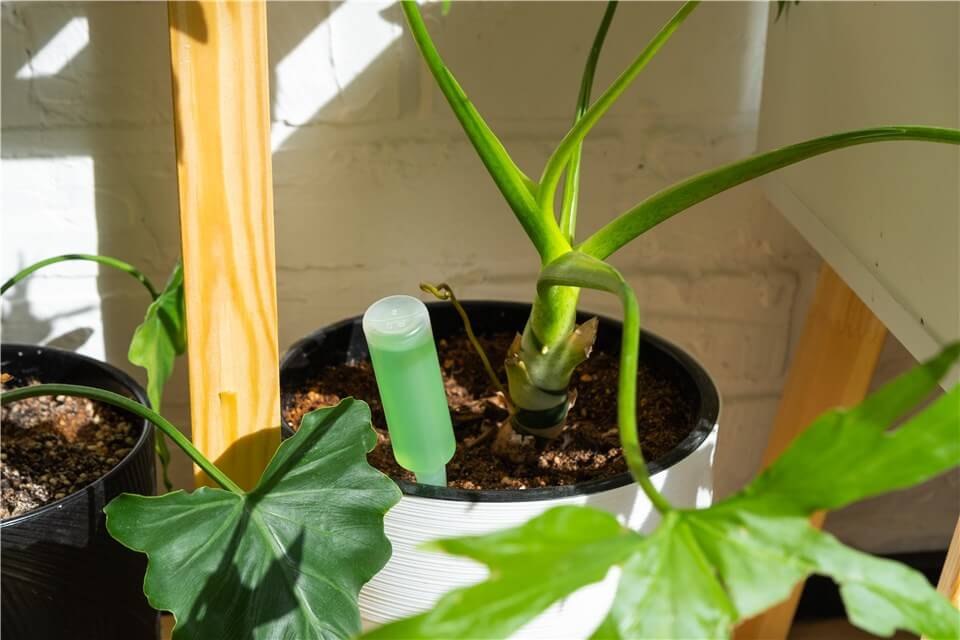

Growth Stimulators for Stunted Growth Plants
Additionally, growth stimulators can improve a plant’s resilience to environmental stresses, such as drought or disease, enabling it to thrive even under challenging conditions. By incorporating growth stimulators into a plant care routine, gardeners can optimize growth rates, increase yields, and foster stronger, more robust plants that are better equipped to withstand pests and diseases. Ultimately, these products help create an environment conducive to rapid and healthy plant development.
Alternate Crops
Alternating crops, or we say crop rotation, can also contribute to faster growth and overall productivity. By planting different crops in succession, farmers and gardeners can improve soil health, reduce pest and disease pressures, and optimize nutrient availability. This practice prevents nutrient depletion that can occur when the same crop is grown repeatedly in the same soil, allowing each type of plant to thrive. Additionally, certain crops can enhance the growth of subsequent plants by fixing Nitrogen in the soil or improving soil structure, ultimately leading to healthier and faster-growing crops.
What Plant Grow Quickly?
If you’re eager to see rapid plant growth and harvest in your indoor garden, try to select fast-growing plants. There is a list of fastest-growing plants that can add beauty and productivity to your garden in no time.
- Bamboo
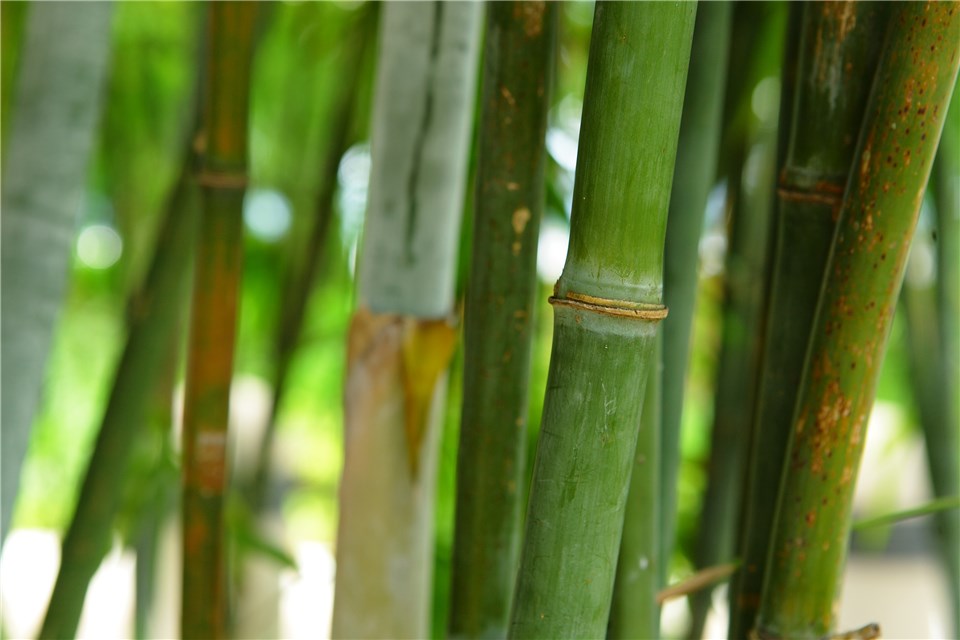

Plant Grows Quickly - Bamboo
Bamboo is renowned for being one of the fastest-growing plants across the globe. Certain species can grow up to 36 inches in a single day under optimal conditions. This makes bamboo an excellent choice for privacy screens and garden structures.
- Sunflower
Sunflowers are stunning and quick to grow, reaching maturity in just 70 to 100 days. Their vibrant blooms can brighten up any garden, and they attract pollinators, making them a great addition to biodiversity.
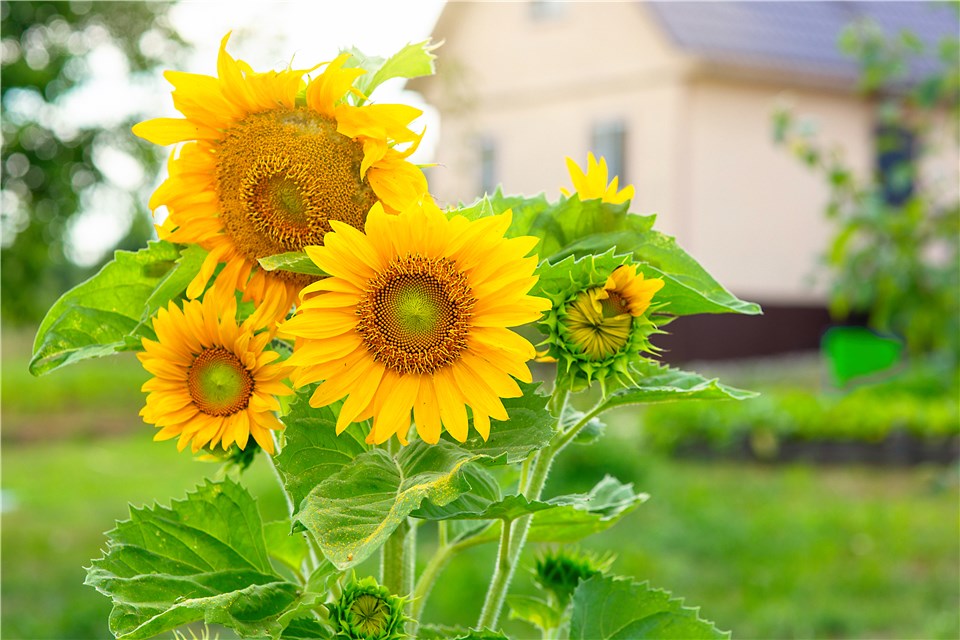

Plant Grows Quickly - Sunflower
- Radishes
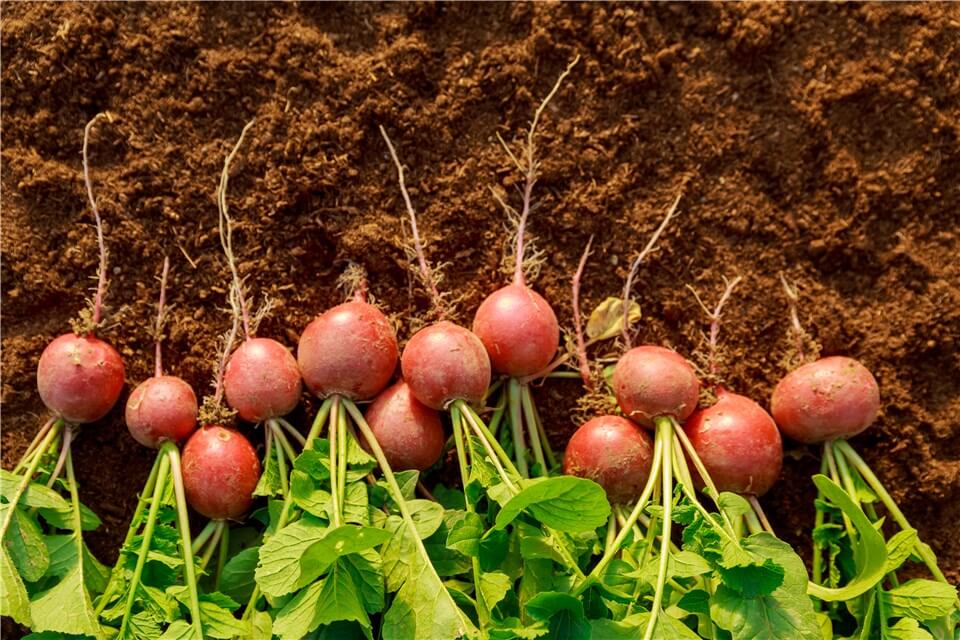

Plant Grows Quickly - Radishes
If you're looking for fast results in your vegetable garden, radishes are a top pick. These root vegetables can be ready to harvest in just three to four weeks, making them perfect for quick meals and a fun choice for beginner gardeners.
- Lettuce
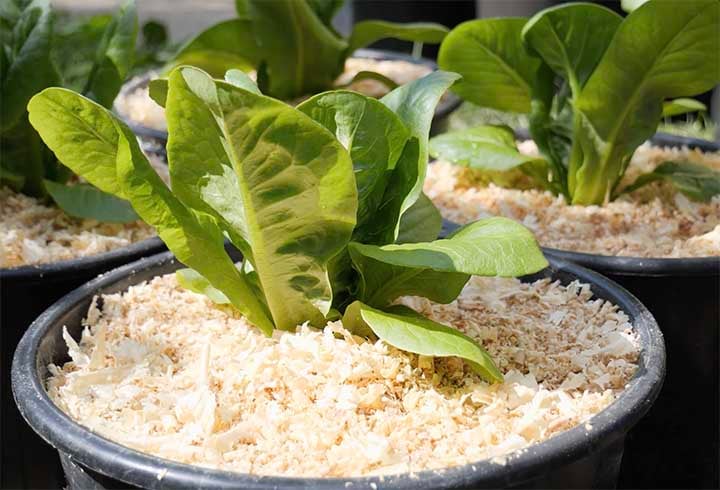

Plant Grows Quickly - Lettuce
Lettuce varieties are known for their rapid growth, typically ready for harvest within 30 to 45 days. With minimal space requirements, lettuce is ideal for container gardening and can provide fresh greens for salads in no time.
- Zucchini
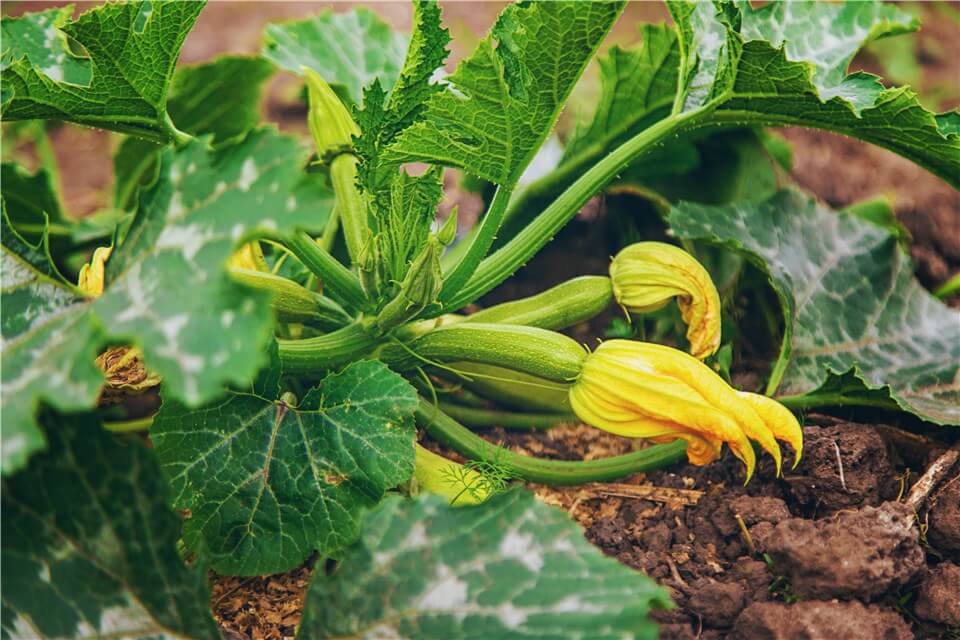

Plant Grows Quickly - Zucchini
Zucchini is a prolific producer that can yield fruit in about 45 to 55 days. This versatile vegetable is not only fast-growing but also easy to cultivate, making it a favorite for home gardeners.
- Cress
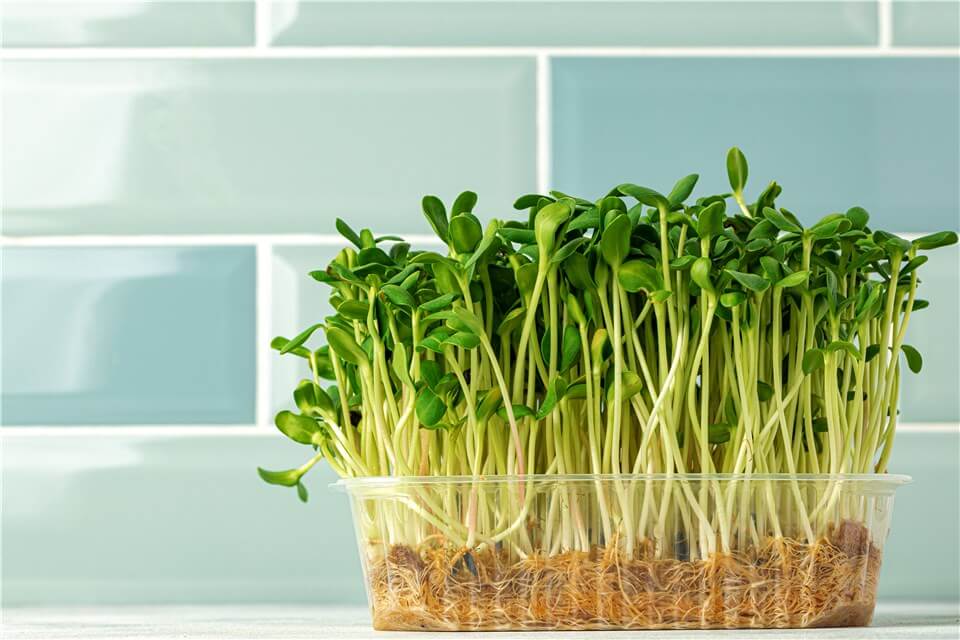

Plant Grows Quickly - Cress
Cress is an incredibly fast-growing leafy green that can be ready to eat in just 7 to 14 days after sowing. It’s perfect for adding to salads and sandwiches, providing a peppery flavor and a nutritional boost.
- Marigolds
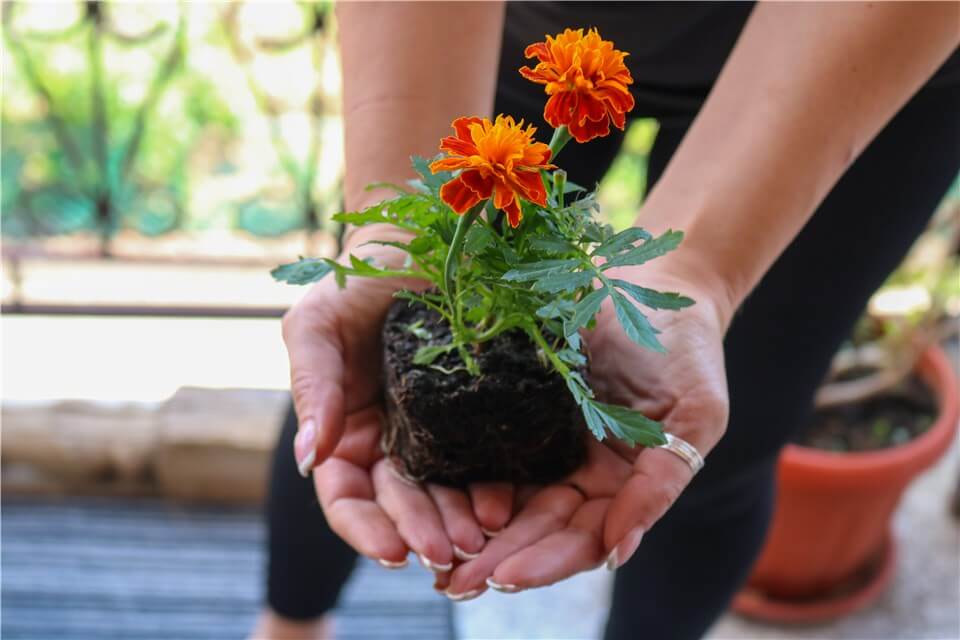

Plant Grows Quickly - Marigolds
For those looking to add color to their garden quickly, marigolds are a fantastic option. These cheerful flowers can bloom within 8 to 10 weeks, making them great for borders and flower beds.
What Plants Grow Slowly?
Plants that grow slowly often require more time to reach maturity. Slowly-growing plants often include varieties like oak trees, which may take decades to fully develop. Cacti grow very gradually in arid environments. Japanese maples are also known for their slow growth, which may take several years to achieve significant height and spread. Additionally, many perennial flowers, such as peonies and bleeding hearts, can take a few seasons to establish before blooming profusely. Slow-growing plants often have unique characteristics, such as deeper root systems and longer lifespans, making them valuable for specific landscaping and gardening needs, even if they require more patience to thrive.
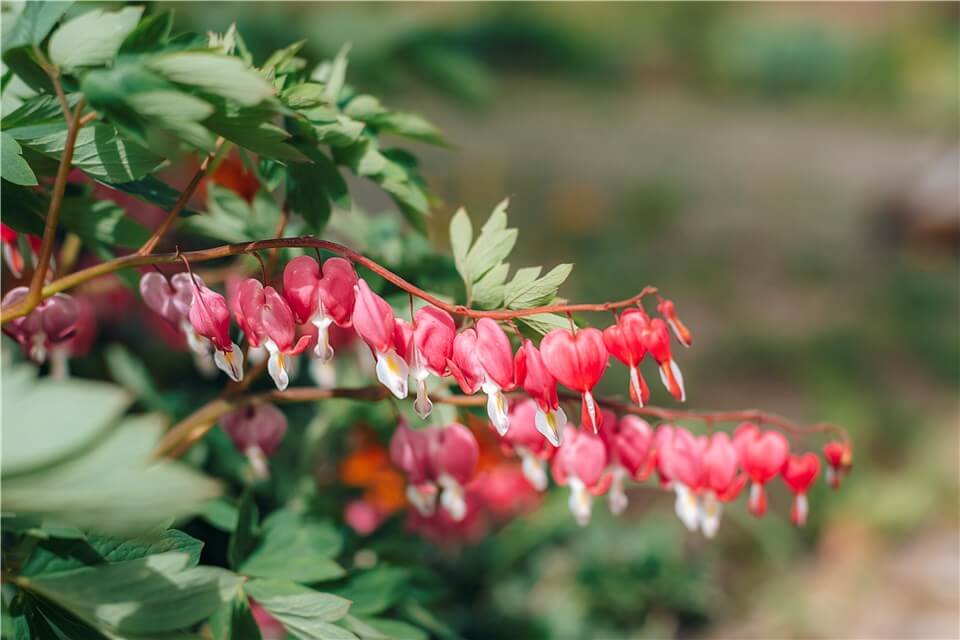

Plants Grow Slowly - Bleeding Hearts
FAQs About Plant Growth
By the end of the post, we’ll address several frequently-asked questions about plant growth.
Do plants grow at night?
Yes, plants do grow at night. Although the process involved differ from those during the day. While photosynthesis normally occurs in the presence of sunlight, plants utilize the energy stored during the day for growth and development at night. This nighttime growth includes vital activities such as cell division and elongation, which are essential for overall plant health. Additionally, plants may engage in respiration and nutrient uptake during the night, allowing them to continue their growth cycle even in the absence of light.
How long does a plant take to grow?
The time it takes for a plant to grow can vary significantly depending on the type of plant, environmental conditions, and care practices. Fast-growing plants, like radishes and lettuce, can mature in as little as three to four weeks, while sunflowers may take 70 to 100 days. On the other hand, slower-growing plants, such as oak trees and certain perennials, can take several years or even decades to reach full maturity. Factors like soil quality, light availability, water, and temperature all play crucial roles in determining growth rates. Overall, the growth timeline varies widely, making it essential to consider the specific needs of each plant type.
How long does flowers take to grow?
The time it takes for flowers to grow can also vary widely depending on the type of flower and growing conditions. Fast-growing annuals, such as marigolds and zinnias, can bloom within 30 to 60 days after planting. In contrast, perennials like peonies or bleeding hearts may take a couple of years to establish and bloom fully. Some biennial flowers, such as foxgloves, typically flower in their second year. Environmental factors like sunlight, soil quality, and water availability also significantly influence growth rates. Overall, while some flowers provide quick results, others require more patience and care to reach their blooming potential.